When your website isn’t being crawled by Googlebot, it can result in decreased visibility and hinder your site’s search engine ranking potential. Identifying and addressing these crawling issues can be both daunting and crucial for your online presence. Fortunately, there are common obstacles and practical solutions that can help you troubleshoot and resolve these challenges effectively. In this article, we’ll explore various fixes ranging from technical SEO adjustments to server settings that might be impeding Google’s ability to crawl your site efficiently. By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your website’s crawlability and improve its search engine performance.
Top Solutions for Googlebot Crawling Issues
1. Check Your Robots.txt File
Make sure your robots.txt file is not disallowing Googlebot from crawling your site. This file instructs search engines which pages they can or cannot visit on your site. Ensure that your robots.txt file is accessible and contains the right directives. You can check and modify it in the root directory of your website. Use the Google Search Console to test your robots.txt and see if it’s blocking any resources unnecessarily.
2. Ensure Your Website Is Not Temporarily Downtime
If your website is experiencing downtime, Googlebot might not be able to access it. Use uptime monitoring tools to check if your site is available. Frequent downtimes can negatively affect how Google crawls your site, so ensuring site stability and performance is crucial.
3. Improve Page Load Speed
Slow-loading pages can discourage Googlebot from crawling your site effectively. Optimize your website speed by compressing images, minifying code, and using browser caching. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can provide insights on how to enhance your page load speed.
4. Review Site Map Configuration
A correct and dynamic site map helps Googlebot understand the structure of your website and find all your important pages. Ensure your site map is up-to-date and correctly submitted to the Google Search Console. Check for errors in your site map file that could potentially hinder crawling.
5. Inspect Your Website for Crawl Errors
Utilize Google Search Console to look into crawl errors. This tool will provide detailed reports on any issues that Googlebot encounters while trying to crawl your site. Fix any 404 errors, server errors, or redirect issues that might be affecting your site’s accessibility.
| Issue | Solution | Tool/Resource |
|---|---|---|
| Blocked by robots.txt | Update and test robots.txt | Google Search Console |
| Downtime | Monitor and ensure site uptime | Uptime Monitoring Tools |
| Slow Load Speed | Optimize site speed | Google PageSpeed Insights |
| Site Map Issues | Update and submit site map | Google Search Console |
| Crawl Errors | Fix errors via console | Google Search Console |
Why is Google not crawling my website?

Technical Issues on Your Website
Sometimes, technical issues can prevent Google from crawling your website effectively. These issues can range from server errors to improper website configurations.
- Robots.txt File: Ensure that your site’s `robots.txt` file is not disallowing pages you want Google to crawl. Check for `Disallow` directives that could block Googlebot.
- Server Errors: If your server frequently goes down or is slow to respond, Google may not be able to access your site. Regularly monitor your server’s performance and uptime.
- Redirects and URL Errors: Misconfigured redirects or error-ridden URLs can also prevent crawling. Tools like Google Search Console can help identify crawl errors and redirect issues.
Website Structure and Content Issues
Google may struggle to crawl your site if there are structural or content issues that affect crawlability and indexing.
- Lack of Internal Linking: Make sure to create a robust structure of internal links. This helps Google understand the hierarchy and relationship between different pages.
- Poor XML Sitemap: An outdated or incomplete XML sitemap can lead to poor crawling efficiency. Ensure your sitemap is updated with all the important pages you want Google to see.
- Thin or Duplicate Content: Pages with thin or duplicate content can negatively impact your crawl budget. Ensure your site contains unique, valuable content.
External Factors or Policies
External issues, such as Google’s algorithms or external penalties, can also affect crawl rates.
- Manual Penalties: If Google has issued a manual penalty on your site, crawling and indexing might be affected. Review Google Search Console for any penalty notifications.
- Algorithm Updates: Changes in Google’s crawling algorithms may impact your site’s crawlability. Stay updated with the latest from Google to adjust your site accordingly.
- Lack of Backlinks: If your site lacks backlinks, Google might perceive it as less authoritative, affecting how often it’s crawled. Work on building quality backlinks.
How to fix crawl error?
Fixing crawl errors is essential for ensuring that your website is properly indexed by search engines, which can affect organic search rankings and visibility. Here’s a step-by-step guide to address these errors:
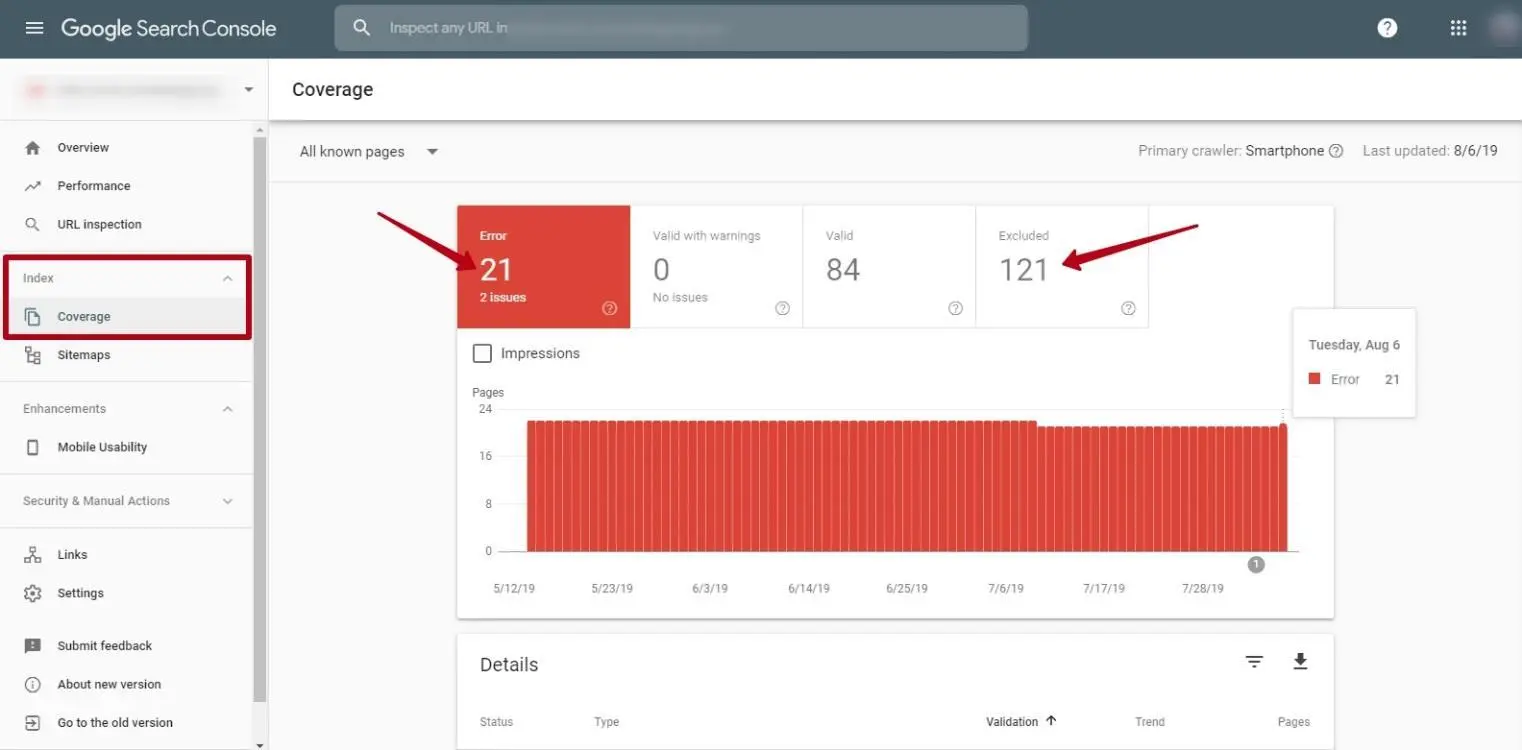
Identify Crawl Errors Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console is an invaluable tool for identifying crawl errors on your site. Here’s how you can use it effectively:
- Log into Google Search Console and select your website.
- In the left sidebar, navigate to Coverage under the Index section. Here you will see errors that Google encountered while crawling your site.
- Pay attention to Error and Excluded sections. Labels such as 404 Not Found or 500 Server Error highlight specific issues to address.
Resolve 404 Not Found Errors
404 errors occur when a browser requests a resource that the server cannot find. Here’s how to fix them:
- Redirect Missing Pages: Employ a 301 redirect to point the old URL to a new, relevant page, which helps in maintaining any acquired link equity. Tools like HTACCESS for Apache Servers can streamline this process.
- Fix Broken Links: Update referring links to the correct URL. Use site audit tools or browser extensions to quickly find these broken links across your site.
- Create Custom 404 Page: Design a user-friendly 404 page to enhance user experience, providing options to navigate back to the homepage or search for content.
Address Server Errors (5xx)
Server errors (5xx) are typically issues from the server side. Here’s how to troubleshoot them:
- Check Server Logs: Review server logs to identify the occurrence and details of the error. This can help in pinpointing the underlying issue.
- Inspect Server Resources: Ensure that your server has adequate resources like RAM and CPU power to handle requests efficiently, as resource exhaustion can frequently cause these errors.
- Consult Hosting Provider: If you cannot resolve server issues internally, reach out to your hosting provider for technical support and consider upgrading your hosting plan if necessary.
How do I stop Googlebot from crawling my site?
To stop Googlebot from crawling your site, you can use several methods to configure your website. Depending on your needs, choose from modifying the `robots.txt` file, using the meta tag approach, or implementing server-side configurations. Here are some effective ways to achieve that:
Modify the robots.txt file
The `robots.txt` file is used to instruct search engine bots on which pages to crawl or not. To block Googlebot specifically, you can:
- Create or edit the `robots.txt` file in the root directory of your website.
- Add the following lines to prevent Googlebot from crawling your entire site:
plaintext
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: / - Save the changes and verify the file to ensure it’s correctly implemented.
Use Meta Tags to Block Crawling
Meta tags can be used to control the crawling and indexing of specific web pages. Here’s how:
- Add a “ tag to the “ section of the HTML of each page you want to block:
- This tag tells search engines that they should neither index the page nor follow the links on it.
- Use this method for individual pages where modifying the `robots.txt` file isn’t practical.
Implement Server-Side Configurations
Server-side configurations add another layer of control for blocking Googlebot:
- Configure your server to return a `403 Forbidden` status code for requests from Googlebot. This can be set up in `.htaccess` or by using server-side scripting.
- For Apache servers, update your `.htaccess` file to include:
plaintextRewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} Googlebot
RewriteRule . – [F,L] - Test the server response to ensure that the block is effectively in place.
How to fix crawled not currently indexed?
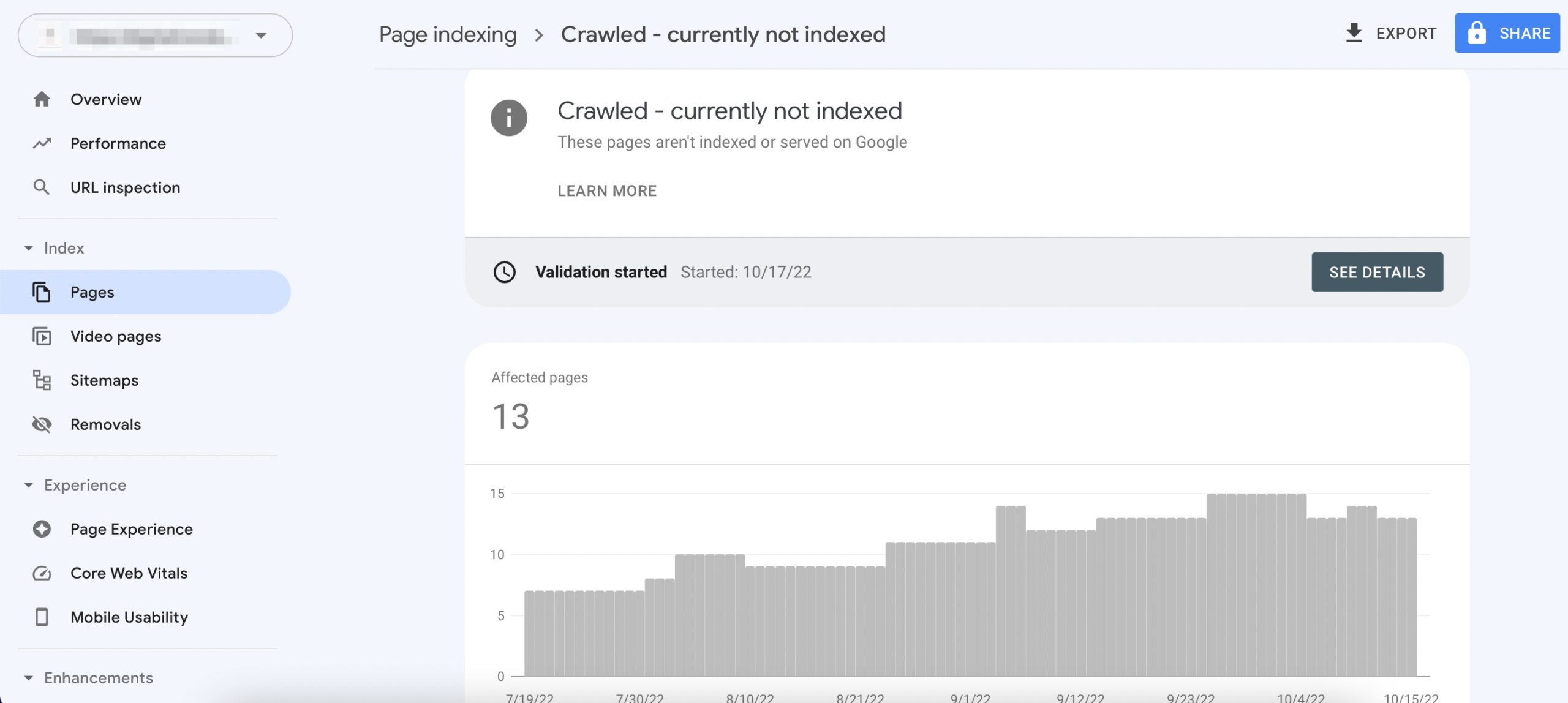
To fix the issue of crawled not currently indexed, there are several strategies and actions you can implement to encourage search engines to index your pages. Here’s a detailed response with subheadings and list formats to address this challenge effectively:
Improve the Quality of Your Content
Enhancing the quality of your content is one of the primary methods to ensure it gets indexed efficiently.
- Ensure Uniqueness: Ensure that your content is original and not duplicated across your domain or other sites. Search engines prioritize indexing original content.
- Incorporate Keywords Naturally: Use relevant keywords throughout your content, but place them naturally to avoid keyword stuffing that might negatively impact indexing.
- Increase Value: Provide comprehensive, insightful information that addresses the needs of your audience. Content that thoroughly covers a topic is more likely to be indexed.
Optimize Technical SEO
Making sure your site’s technical aspects are in order is crucial for search engine indexing.
- Check Site Structure: Ensure that your website’s structure is clean and logical. This helps crawlers navigate efficiently through your site.
- Use XML Sitemaps: Keep your XML sitemap updated with all the pages you want to be indexed and submit it to Google Search Console to aid in indexing.
- Avoid Crawl Errors: Regularly check for and fix any crawl errors. Tools like Google Search Console will help identify these issues.
Enhance Site Engagement
Improving user engagement metrics can also encourage search engines to index your content.
- Boost Page Loading Speed: Improve the page load times to retain visitors and reduce bounce rates, which can positively influence indexing.
- Encourage Social Sharing: Use social media to drive traffic to your site and increase its visibility, which can prompt indexing.
- Improve User Experience: Make sure your site is easy to navigate and visually appealing to keep users engaged, which can lead to better indexing rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why isn’t Googlebot crawling my site?
There could be several reasons why Googlebot isn’t crawling your site. First, you might have a robots.txt file that inadvertently blocks Googlebot from accessing your site. Additionally, if your site is experiencing server issues or is frequently down, Googlebot may be unable to access your pages. It’s also possible that your website doesn’t have sufficient backlinks, making it less visible to Google’s crawlers. Check for manual actions in your Google Search Console, as these can prevent indexing and crawling. Lastly, be sure your website is not using any incorrect redirections or missing metadata that could confuse the bot.
How can I check if Googlebot has access to my site?
To verify if Googlebot can access your site, you can start by using the robots.txt Tester found in the Google Search Console. This tool helps you ensure your robots.txt file isn’t inadvertently blocking URLs you want Googlebot to crawl. Another method is to use the URL Inspection tool in the Search Console to see how Googlebot views your specific pages. Moreover, check your server logs for activity from Google’s user-agent to confirm that crawling requests are reaching your server. These steps will provide an overview of how Googlebot is interacting with your site and allow you to make adjustments if necessary.
What steps should I take to ensure my site is crawl-friendly?
To make your site crawl-friendly, start by ensuring that your robots.txt file properly allows access to key areas of your site. Check that there are sitemaps submitted to Google and that these are up-to-date and complete. Incorporate an effective internal linking structure to help Googlebot smoothly navigate through your pages. Keep your website’s loading speed optimized, as slow site speeds can cause crawlers to abandon the process. Finally, confirm that you have no crawl errors listed in your Google Search Console, and regularly update your site’s content to keep Googlebot interested in ongoing crawling.
What should I do if Googlebot hasn’t crawled my site for a long time?
If Googlebot hasn’t crawled your site for a long time, it’s crucial to check your site’s crawl budget and ensure that you’re not inadvertently exhausting it. You should also verify that your robots.txt file is correctly configured to allow Googlebot’s access wherever desired. Use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to request indexing for any new or updated pages. Additionally, resolve any server errors that might inhibit crawling and improve your site’s performance to make it more appealing for regular visits by the bot. If problems persist, you can submit a reconsideration request through the Search Console, especially if manual actions are present affecting visibility and indexing.

