In the fast-paced world of digital marketing, businesses often focus on achieving top search engine rankings, believing this will lead to greater visibility and traffic. However, before a site can rank, it needs to be indexed by search engines, making indexing a crucial first step in any search engine optimization (SEO) strategy. Indexing allows search engines to understand and catalog the content on a website, determining how and where it should appear in search results. This article explores why prioritizing indexing over immediate rankings can lead to more sustainable and effective SEO outcomes, setting the foundation for long-term success.
The Foundations of Digital Visibility: Understanding the Role of Indexing
Understanding the importance of indexing before focusing on ranking is crucial in the realm of search engine optimization (SEO). When a website is indexed, it means that its content has been discovered and analyzed by search engines, making it available within their systems. Without indexing, it is impossible for a page to achieve any meaningful ranking. Thus, indexing serves as the gatekeeper to visibility, ensuring that a website is accessible to the audience it is intended to reach.
What is Indexing and Why Does It Matter?
Indexing is the process by which search engines like Google crawl the web and add new content to their databases. During this process, search engines collect, parse, and store data from websites, enabling users to find these sites through search engine results. Indexing is the crucial first step in the mechanism of search engines, much like libraries catalog books. Without being indexed, a website cannot appear in search engine results, rendering it invisible to users searching for relevant information. Therefore, when websites focus on being indexed properly, they set the foundation for building online presence and authority.
How Does Indexing Differ from Ranking?
While both indexing and ranking are essential elements of SEO, they serve different purposes. Indexing is about getting your website content into the search engine’s database, whereas ranking pertains to the position at which your content will appear on the search engine results pages (SERPs). Think of indexing as registering for a library’s database, while ranking is akin to where on the library’s shelves a book is placed and how easily it can be found. Without proper indexing, a page has no opportunity to rank, as search engines won’t recognize or prioritize unindexed content.
The Technical Aspects of Indexing
Successful indexing involves several technical elements. First, the use of sitemaps and robots.txt files guides search engine bots to the appropriate pages for indexing. Furthermore, structured data and metadata enhance indexing efficiency by providing search engines with better context and understanding of the page content. Websites should ensure that pages are not restricted from indexing unless deliberately decided. Regularly checking Google Search Console for errors and potential impediments can help maintain proper indexing. The foundation of good indexing is consistency and accuracy in technical configurations.
Challenges with Indexing New Content
One common challenge with indexing new content is the time it takes for search engines to recognize and process new information. There are often delays between content publication and when it becomes searchable. This is particularly evident with websites that launch significant content updates or new pages. Additionally, websites may face indexing issues due to poor site structure, server issues, or improper use of directives that block bots. Understanding how these technical barriers impact indexing helps SEO practitioners address them effectively. Ensuring quick and accurate indexing requires ongoing monitoring and proactive adjustments.
Best Practices to Enhance Indexing
To enhance indexing efficiency, websites should employ best practices such as regularly updating content, ensuring clear site architecture, and optimizing site speed. Having a robust, mobile-friendly design is also necessary since mobile indexing is now prioritized by many search engines. Using internal links strategically can guide search engines to discover deeper or less visible content within a site. Ensuring high-quality backlinks can also signal to search engines the importance and relevance of new content. These practices collectively enhance a site’s potential to be indexed promptly and completely.
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Indexing | Enables search engines to discover and list new website content. |
| Ranking | Determines the visibility of content within search outcomes. |
| Technical Elements | Utilization of sitemaps, structured data, and robots.txt to facilitate indexing. |
| Challenges | Delay in processing new content and issues with site configuration. |
| Best Practices | Regular updates and strategic internal linking bolster indexing processes. |
Why is indexing so important?

Improved Access to Information
Indexing plays a crucial role in the organization of information, making it easier for users to find specific data quickly.
– Efficient Retrieval: Indexed data allows for direct access, bypassing irrelevant data and reducing the time needed for search.
– Structured Navigation: An index provides a structured way to navigate large amounts of information, similar to a table of contents.
– User Experience: Improved search capabilities enhance user experiences by facilitating faster and more accurate results.
Enhancement of System Performance
Indexing significantly contributes to the performance efficiency of databases and data storage systems.
– Speed Optimization: By reducing the amount of data scanned during queries, indexing increases the speed of data retrieval.
– Resource Management: Indexes help in efficient utilization of system resources, preventing unnecessary load and maintaining system health.
– Scalability: As data grows, indexed systems can handle large volumes better, supporting scalability without a performance hit.
Accuracy and Reliability in Searches
Indexes ensure that searches are not only fast but also accurate and reliable.
– Precision: Indexing ensures that queries return precise results by narrowing down the dataset efficiently.
– Consistency: Repeated searches provide consistent results due to the organized data structure.
– Error Reduction: With adequate indexing, the risk of retrieving incorrect data is minimized, bolstering data reliability.
What is the difference between ranking and indexing?
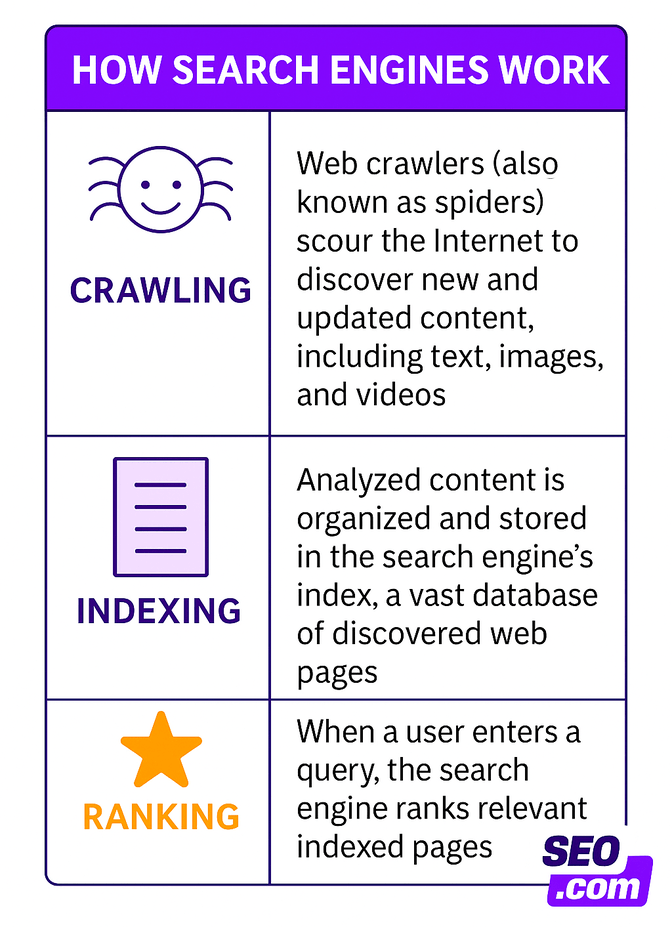
The Concept of Indexing
Indexing is a fundamental step in search engine processes and involves the collection, parsing, and storage of data to facilitate speedy and effective information retrieval.
– Data Collection: Web crawlers, also known as spiders, traverse the web to gather pages to be indexed.
– Parsing Content: The gathered data is analyzed to determine relevant keywords and metadata.
– Storage: The processed information is stored in a structured database, allowing a search engine to quickly pull relevant information.
The Process of Ranking
Ranking occurs after indexing and involves determining the order of search results based on their relevance to a user’s query.
– Algorithm Evaluation: Search engines use algorithms to evaluate the indexed content against the search query.
– Relevance Assessment: Various factors, such as keyword usage, backlinks, and content quality, are considered.
– Result Ordering: The most relevant results are displayed at the top, ordered based on the evaluation scores.
Key Differences Between Indexing and Ranking
While both indexing and ranking are crucial to search engine functionality, they differ in purpose and process.
– Purpose: Indexing organizes data to make it searchable, whereas ranking orders the results for presentation.
– Process: Indexing involves storage and ensures all web pages are logged, while ranking evaluates and orders these pages.
– Result Impact: Indexing affects breadth and inclusion scope, while ranking impacts visibility and user engagement.
What happens first, crawling or indexing?
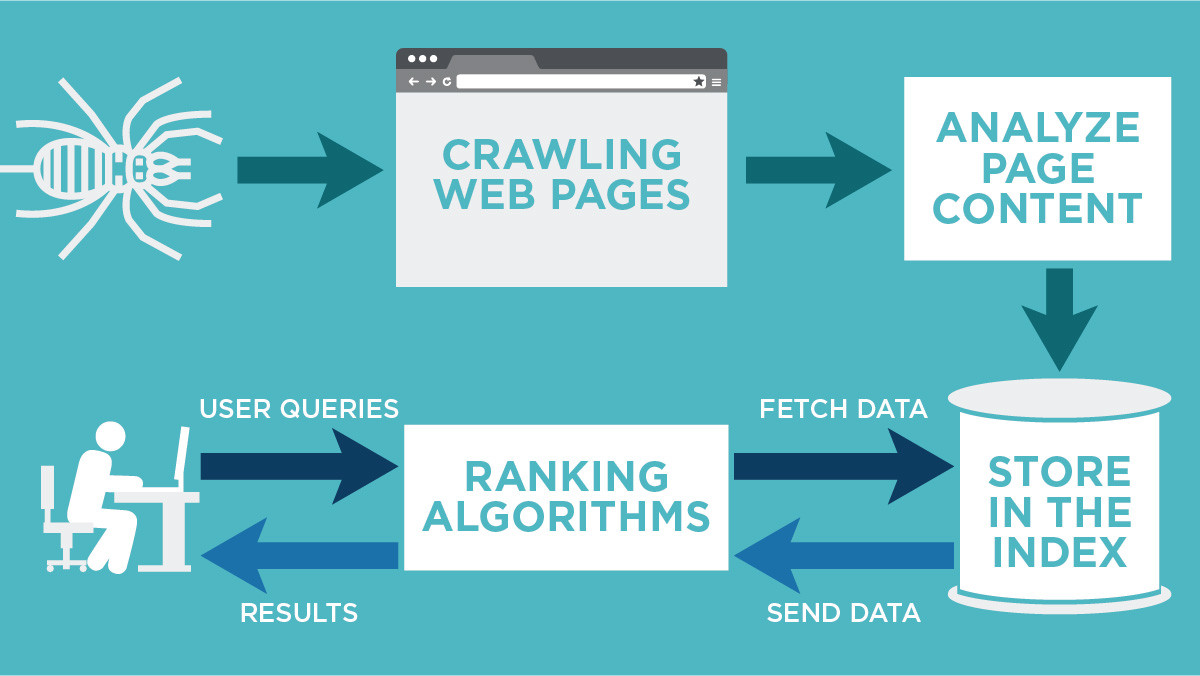
Crawling: The First Step
Crawling is the initial phase in the process of web searching, undertaken by search engine robots known as crawlers or spiders. During this phase, these crawlers traverse the internet to discover new and updated content. Here’s how it works:
- Discovery: Crawlers use a web crawler algorithm to discover URLs and find new web pages or changes to existing ones.
- Following Links: They navigate by following hyperlinks from already known sites, expanding their reach across various web pages.
- Site maps: Webmasters can provide a site map, which is a guide for crawlers to understand all the URLs that need crawling within a website.
Indexing: The Subsequent Stage
Once the crawling process is completed, indexing is the next step where the gathered data is organized within a database known as an index. This helps search engines retrieve information swiftly and efficiently:
- Content Analysis: The crawled data is analyzed to understand the content and context of each webpage.
- Storage: Relevant keywords, the location of words, and other metadata are extracted and stored in the search engine index.
- Information Retrieval: The indexed pages become part of a database that helps search engines quickly present the most relevant results to user queries.
Why Crawling Precedes Indexing
Crawling must occur before indexing because it is essential for discovering and compiling the web pages that will be indexed. Each step has its unique role:
- Prerequisite: You cannot index what has not been crawled. Therefore, crawling serves as a necessary prerequisite to indexing.
- Organizational Need: Indexing organizes data after it has been collected by crawling, ensuring the information retrieval process is efficient.
- Content Verification: Before information is organized in an index, it must be verified and processed during the crawling stage.
What is mobile first indexing and why is it important?

Mobile-first indexing refers to the approach where Google predominantly uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking. Historically, the index primarily used the desktop version of a page’s content, but as the mobile usage increased and became the main driver of traffic, Google shifted to this method to ensure a site’s mobile presence is as robust as its desktop presence.
Why Mobile-First Indexing is Essential
The importance of mobile-first indexing can be attributed to several key factors:
- User Experience: With the majority of users accessing websites via mobile devices, having a site optimized for mobile ensures a better user experience. This can lead to increased engagement and lower bounce rates.
- Search Rankings: Websites optimized for mobile are likely to rank better in search results. A mobile-friendly site ensures improved visibility on Google, which can significantly impact traffic.
- Market Trends: With the ubiquity of smartphones, adapting to a mobile-first approach aligns with consumer behavior. Businesses can tap into a larger audience by optimizing for mobile users.
Impact of Mobile-First Indexing on SEO
Mobile-first indexing has transformed the SEO landscape in several ways:
- Responsive Design: It emphasizes the need for responsive design that caters to all device types. Websites must automatically adjust to various screen sizes to pass Google’s mobile-friendly tests.
- Page Speed: Site speed is a critical factor, especially on mobile. Slow loading times can lead to poor rankings as Google prioritizes fast-loading mobile experiences.
- Content Consistency: Ensuring parity between the mobile and desktop versions of a site is crucial. Content accessible on the desktop must also be available and easily interactable on the mobile version.
How to Adapt to Mobile-First Indexing
For websites to effectively adapt to mobile-first indexing, they should consider the following strategies:
- Mobile-Focused Content: Prioritize concise and impactful content that can be easily read on smaller screens. Avoid bulky images and large files that could hinder performance.
- Technical SEO Adjustments: Utilize tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to identify potential issues. Ensure proper use of meta tags, structured data, and robot.txt settings in the mobile version.
- User Testing: Conduct regular user testing on mobile devices to identify and resolve usability issues. User feedback can provide insights into what aspects of the mobile experience need improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between indexing and ranking in SEO?
Indexing and ranking are two fundamental aspects of SEO, yet they serve different purposes. Indexing involves the process by which search engines like Google gather, parse, and store information from websites. When a website is indexed, it becomes part of the search engine’s database. The pages then become eligible to appear on search engine results pages (SERPs). In contrast, ranking refers to the position a webpage holds on those SERPs for specific keywords or queries. While indexing is about inclusion in the search system, ranking concerns the visibility and competitiveness of the content against numerous other indexed sites for given phrases or questions.
Why is focusing on indexing more important initially than ranking?
Before a website can even think about high rankings, it first needs to be indexed. If your content is not indexed, it means search engines are not aware of its existence, and thus it cannot be ranked at all. Prioritizing indexing ensures that your website is being recognized and stored within the search engine’s database. This foundational step is crucial because if your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t show up in search results at any ranking position. Moreover, indexing provides a platform upon which you can develop advanced SEO strategies to improve your ranking over time. Thus, focusing on effective indexing practices initially lays the groundwork for more successful ranking efforts later on.
How can one ensure a website is indexed effectively by search engines?
To ensure effective indexing by search engines, there are several best practices you should follow. First, create a comprehensive sitemap that tells search engines about the structure of your website and the most important pages. Submitting this sitemap through tools like Google Search Console can significantly help. Ensure that your website has a clean, crawl-friendly architecture meaning that the navigation is clear, and important pages are accessible within a few clicks of any homepage. Moreover, websites should avoid duplicate content and use the correct canonical tags to guide search engines on the content they should index. Quality content, fast page load speeds, and secure website protocols (HTTPS) are also critical for encouraging search engines to prioritize your pages for indexing.
What common mistakes can hinder a website’s ability to get indexed?
Several common mistakes can obstruct a website from getting properly indexed. One major issue is having a disallow directive in the robots.txt file, inadvertently preventing search engines from crawling parts of or the entire website. Likewise, not clearly defining canonical URLs can confuse search engines and lead to improper indexing of duplicate or similar content. Another common mistake involves sloppy internal linking, which can obstruct search engines from efficiently finding and evaluating new or updated content. Additionally, relying too heavily on pages that only exist through search or user input can make those pages inaccessible to search engine crawlers. These mistakes, along with having thin content with little or no unique value, can significantly hinder a site’s indexing efforts.

