In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing and search engine optimization (SEO), the concept of indexing and crawl budget optimization has gained prominence as critical components for enhancing online visibility. Search engines crawl and index billions of web pages, but not all get equal attention. Efficiently managing how search engine bots prioritize your site’s content is crucial for maximizing exposure. Understanding the interplay between indexing and the crawl budget can significantly impact the frequency and efficiency with which your website is explored, ultimately influencing its search ranking and visibility. This article delves into the essentials of optimizing these elements for better SEO performance.
The Link Between Indexing and Crawl Budget Optimization
Indexing and crawl budget optimization are two critical components of effective SEO strategy. Understanding how they relate to each other can significantly enhance a website’s visibility and efficiency in search engine listings. Below are detailed explanations of key aspects of this relationship.
What is Indexing?
Indexing is the process by which search engines organize and store information from the web. After a website is crawled, its content needs to be indexed, enabling the search engine to deliver relevant results promptly when users perform searches. This involves analyzing text, images, and meta tags, and assessing relevance and quality. Being correctly indexed is crucial for ensuring that your content is discoverable in search engine results.
Understanding Crawl Budget
Crawl Budget refers to the number of pages a search engine will crawl on your site during a given timeframe. Determined by factors like crawl rate limit and crawl demand, it is finite and influenced by website popularity and health. Managing crawl budget effectively ensures that all essential pages are indexed by search engines, boosting your site’s accessibility and performance in search results.
How Indexing Affects Crawl Budget
The connection between indexing and crawl budget optimization is vital. When a website has too many low-quality or duplicate pages, it can waste crawl budget, preventing more important pages from being indexed. Optimizing your website’s structure and content can reduce unnecessary crawls and ensure that search engine bots are focusing their resources on pages that really matter.
Strategies for Optimizing Crawl Budget
To optimize your crawl budget, focus on: 1. Prioritizing important content: Implement methods like URL parameter tools to direct crawlers to valuable pages first. 2. Reducing duplicate content: Use canonical tags and redirects to prevent the duplication of content and focus the crawl on unique pages. 3. Improving site health: Regularly fixing errors and speeding up page load times enhance overall crawl efficiency. 4. Updating sitemap and robots.txt: Keeping these files up-to-date helps crawlers understand which pages to prioritize and which to ignore.
Impact of Crawl Budget on Search Rankings
Though not a direct ranking factor, the management of crawl budget can significantly affect search rankings. Effective optimization ensures that important pages are indexed more frequently and potential issues are discovered and rectified quicker. Consequently, this can improve a website’s performance in search rankings by making sure that the latest and most relevant content is available to users.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Indexing | The process of storing and organizing web content by search engines. |
| Crawl Budget | The number of pages a search engine will crawl on a website within a set timeframe. |
| Optimization Strategies | Techniques such as prioritizing important content and reducing duplicates to enhance crawl efficiency. |
| Site Health | The overall condition of a website, including factors like error rates and load times, impacting crawl efficiency. |
How do crawling and indexing work together?
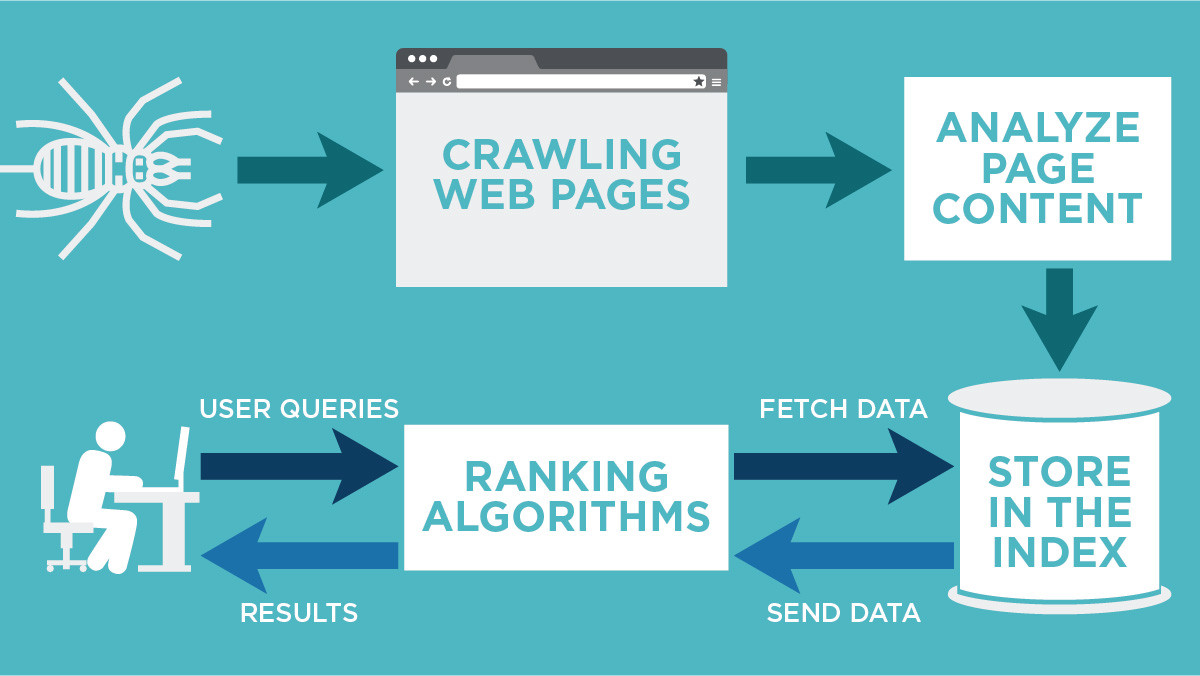
Crawling and indexing are essential processes in how search engines manage and deliver web content. They work in tandem to ensure that users can find relevant information when they perform a search.
What is Crawling?
Crawling is the initial step where search engines discover web pages on the internet. It involves:
- Finding New Content: Search engines use programs called web crawlers or spiders that traverse the web to find new or updated content.
- Following Links: These crawlers follow links from known pages to discover additional pages.
- Gathering Data: During crawling, data of the page is collected and sent back to the search engine to be processed.
What is Indexing?
Indexing follows crawling and involves processing and storing the data collected by crawlers. It ensures that the information is searchable:
- Processing Content: The content from each crawled page is analyzed and stored in an index.
- Storing Data: Indexes contain all the discovered URLs along with relevant signals such as keywords and content freshness.
- Retrieving Information: When a search is conducted, the index is queried to return the most relevant results based on the search query.
How Do Crawling and Indexing Work Together?
Crawling and indexing are interconnected and operate in a streamlined process:
- Interdependence: Crawling gathers the content that is essential for indexing, while indexing organizes the information collected by crawlers.
- Efficiency: Effective crawling ensures that all relevant pages are indexed, which subsequently allows for accurate searches and retrieval of information.
- Updated Information: Regular crawling ensures the index remains current, reflecting any changes or updates to web pages over time.
What are the two main factors that determine crawl budget?

What is Crawl Budget Allocation?
Crawl budget allocation refers to the amount of resources that search engines allocate to crawl a specific website. It determines how frequently a site is scanned and how many pages are indexed. Here are several key aspects of crawl budget allocation:
- Crawl Rate Limit: This controls the speed of the crawling process to prevent overloading the site’s server, ensuring that it remains functional while the search engine bots are active.
- Content Update Frequency: Sites that update their content more frequently or have fresh content are often crawled more often.
- Server Performance: Websites with faster server responses and lower error rates typically receive a higher crawl budget.
Why Crawl Demand Matters?
Crawl demand is crucial as it affects which parts of a site are visited more frequently, based on user interest and content freshness. The demand can be driven by:
- User Interest: Pages that attract high user engagement or search queries are more likely to be prioritized for crawling.
- Content Changes: Newly updated or added content may increase the demand for crawling as the search engine aims to provide the latest information.
- Page Popularity: Links from other popular websites can elevate the demand for crawling those specific pages.
The Impact of Server Performance on Crawl Budget
Server performance significantly impacts how efficiently a website can be crawled. Search engines aim not to overwhelm servers, thus:
- Response Time: Faster response times ensure that the crawl budget is utilized effectively as bots can retrieve more pages in a shorter period.
- Error Rates: High error rates from a site might lead to a reduced crawl budget to avoid crawling pages that are likely to be inaccessible or malfunctioning.
- Optimized Server Configuration: Well-configured servers that can handle larger traffic typically receive more extensive crawling activities from search engines.
What is the difference between crawling and indexing?

Understanding the Role of Crawling in Search Engines
Crawling is a fundamental process used by search engines to discover and collect data from web pages across the internet. Here’s a detailed explanation of crawling:
– Definition: Crawling involves automatic programs, often called crawlers or spiders, that access and fetch information from various web pages.
– Primary Purpose: The main goal of crawling is to find new or updated web pages and gather the necessary data so that it can be processed and added to the search engine’s index.
– Crawling Process:
- Start: The crawler begins with a list of URLs from previous crawls and sitemap submissions.
- Fetch: The crawler visits each URL, fetching the page’s HTML to examine its content.
- Follow Links: While parsing the fetched pages, the crawler identifies new links and adds them to its list for future crawling.
Indexing: Organizing Information for Retrieval
Indexing is the process of organizing and storing the vast amount of data obtained during crawling. This organization is crucial for efficient information retrieval.
– Definition: Indexing involves analyzing the content gathered during crawling and storing it in a structured database, ready to be served to users during a search query.
– Purpose: The aim is to efficiently categorize and store web page content so that it can be quickly retrieved when a relevant search is performed.
– Indexing Process:
- Content Analysis: Search engines analyze the text, metadata, and other elements from the crawled pages.
- Database Storage: The relevant information is stored in a search engine’s index, a vast database that allows for fast retrieval.
- Ranking Algorithms: Some indexing processes apply algorithms to determine the potential relevance of a page for varying queries.
Key Differences Between Crawling and Indexing
While both processes are essential to how search engines operate, they serve distinct purposes.
– Function: Crawling is about discovery and data collection, whereas indexing focuses on organization and storage.
– Process: During crawling, search engines discover URLs and gather page data; in indexing, this data is sorted and stored in databases for future searches.
– Outcome:
- Crawling determines what pages will be considered for indexing.
- Indexing decides how pages are stored and retrieved efficiently during search queries.
- Crawling can be seen as a map-building exercise, while indexing is the process of filing information in a detailed catalog.
What is the crawl budget index?
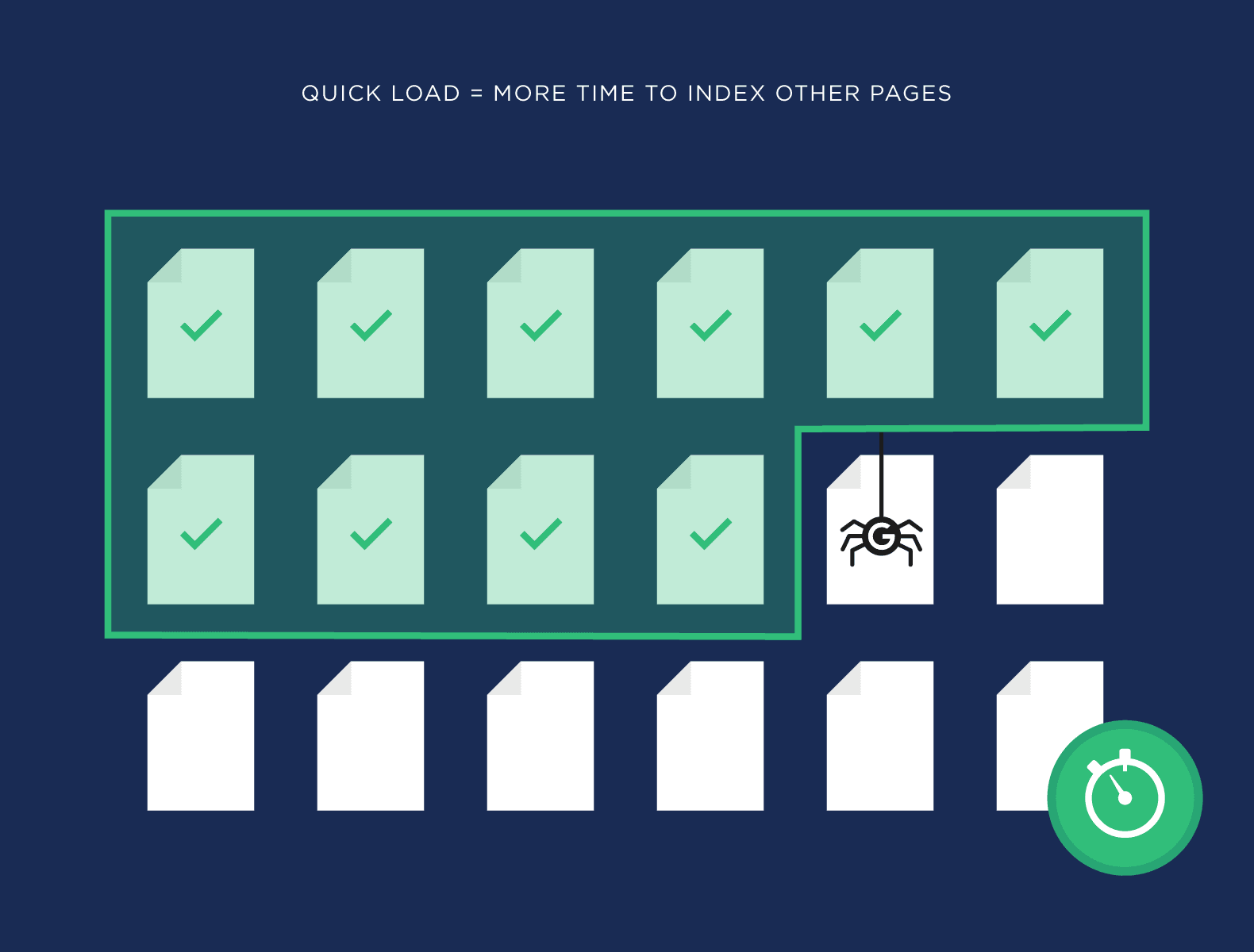
The crawl budget index refers to the resources and frequency at which search engines like Google crawl and index a website’s content. This index is crucial for website owners and SEO specialists to understand, as it directly impacts how quickly and effectively a website’s pages are indexed in search engines. A well-optimized crawl budget ensures that important pages are indexed and available to users in search queries, whereas a poor crawl budget can result in delayed indexing or overlooked pages.
Factors Influencing Crawl Budget Index
Several factors can affect a website’s crawl budget:
- Page Popularity: Highly popular pages often have a higher crawl budget because search engines prioritize pages that users visit frequently.
- Internal Link Structure: A well-structured internal link system helps search engine bots discover and crawl pages efficiently, thereby improving the crawl budget index.
- Duplicate Content: Eliminating or minimizing duplicate content can free up crawl budget by ensuring that bots spend time crawling unique pages.
Optimizing Crawl Budget for Better Indexing
To optimize your crawl budget, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Improve Site Speed: Faster load times can enhance crawl efficiency and increase the number of pages crawled within a budget.
- Use Robots.txt Files Wisely: Properly configured robots.txt files can guide search bots to prioritize critical pages over less important ones.
- Maintain a Clean Sitemap: A current and accurate sitemap supports search engines in identifying which pages should be crawled and indexed.
Monitoring Crawl Budget through Google Search Console
The Google Search Console is an invaluable tool for keeping track of your site’s crawl budget:
- Crawl Stats Report: This report provides detailed information about the number of requests made by Googlebot and the response of your website.
- Index Coverage Report: Use this feature to identify and rectify issues related to your site’s indexed pages.
- Error Alerts: Receive alerts for any crawling or indexing errors that need immediate attention to ensure the effective use of your crawl budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between indexing and crawl budget optimization?
The connection between indexing and crawl budget optimization is integral to effective SEO strategies. Indexing refers to the process by which search engines like Google store and organize content they discover on the web, making it findable by users. On the other hand, crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine will crawl on a site within a given time. Efficient crawl budget optimization ensures that search engines spend their resources judiciously by focusing on the most relevant and updated content, which in turn increases the likelihood of proper indexing. When the crawl budget is optimized, important pages get indexed faster, ensuring that your site’s content is more readily accessible to users searching for related terms. This process involves removing duplicate content, minimizing redirect chains, and ensuring your website’s architecture is straightforward, leading to a more effective indexation by search engines.
How can poor indexing affect a site’s crawl budget?
Poor indexing can have a detrimental effect on a site’s crawl budget because it can lead to inefficient use of search engine resources. If a site is cluttered with duplicate content or a vast number of low-quality pages, these elements can consume a large portion of the crawl budget without adding any real SEO value. As a result, search engines may spend unnecessary time processing these redundant or unimportant pages instead of focusing on high-quality, essential content. This inefficiency not only limits the chances of getting new and crucial content indexed but can also affect how search engines perceive the quality of a site overall. Ensuring each page is unique, relevant, and provides value can help direct the crawl budget towards pages that truly matter and should be indexed, thus optimizing the entire process.
What strategies can be implemented to optimize crawl budget and improve indexing?
There are several strategies that can be implemented to optimize crawl budget and enhance indexing effectiveness. One key strategy is to eliminate duplicate content within a website, as duplicated pages can unnecessarily exhaust the crawl budget. Implementing canonical tags can also help inform search engines of the preferred versions of pages to index. Improving website speed not only enhances user experience but also ensures that search engines can crawl more pages in the same amount of time, thus maximizing the crawl budget. Focusing on high-quality content is essential: pages that offer unique, valuable information are more likely to get indexed and rank well. Regularly updating content and removing obsolete pages helps maintain the website’s relevance and ensures search engines allocate crawl budget to the most current information. Logical site architecture and a clean sitemap further direct search engines efficiently through a website, promoting better indexation.
Why is monitoring crawl budget vital for indexing optimization?
Monitoring crawl budget is crucial for indexing optimization because it offers insights into how efficiently search engines are interacting with your website. Understanding crawl budget dynamics allows webmasters to assess whether important pages are being crawled and indexed appropriately. For instance, if the crawl budget is being wasted on low-priority or redundant pages, efforts can be made to correct such inefficiencies, potentially leading to improved overall site performance in search results. Monitoring also helps identify technical issues such as broken links, server errors, or other crawling obstacles that might be hindering indexing. By analyzing how search engines allocate their resources on a site, adjustments can be made to ensure that the most critical content is accessible and discoverable, ultimately enhancing visibility and reach in search engine results pages (SERPs). Regular monitoring thus supports sustainable improvements in indexing and ensures that SEO efforts align with business objectives.

