In today’s digital age, search engines play a pivotal role in directing the vast flow of online information. Two giants, Google and Bing, stand at the forefront, each employing unique strategies to index the web’s infinite content. Understanding how these search engine titans differ in their approach to indexing can provide valuable insights for webmasters and digital marketers striving to enhance their online visibility. This article delves into the intricacies of Google and Bing’s indexation processes, exploring elements such as crawling efficiency, ranking algorithms, and content prioritization, offering a comprehensive comparison that underscores the strengths and weaknesses of each platform.
Understanding the Indexation Process in Google and Bing
Google and Bing, the two dominant search engines, utilize distinct methods for indexing the vast array of information available on the internet. Indexation is a key process in how these search engines understand and catalog web content, ultimately affecting how sites are ranked and retrieved in search results.
1. Crawling Mechanisms
Search engines rely on crawlers or bots to navigate and collect data from websites to be indexed. Google’s primary crawler is known as Googlebot, which is highly efficient and emphasizes the discovery of fresh, new content. Googlebot uses sophisticated algorithms to prioritize which sites to crawl more frequently based on factors like website authority and freshness of content. Conversely, Bingbot, the equivalent for Bing, has its own set of criteria and tends to focus more on learning how humans engage with content and less on the sheer volume of pages indexed.
2. Handling JavaScript and Dynamic Content
Google extensively supports the crawling of JavaScript and is continually advancing its capabilities in handling complex and dynamic web pages, allowing such pages to be well-indexed. Bing, traditionally weaker in handling JavaScript, is improving, but challenges remain with fully indexing dynamic content on the same level as Google. Google’s advanced JavaScript rendering often allows it to index content that may not be visible in Bing search results.
3. Content Quality and Relevance Criteria
Google stresses the importance of content quality and frequently updates its algorithms to ensure that high-quality content ranks well. Factors such as E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) are crucial. Bing, while also valuing quality, places significant emphasis on content relevancy and social signals to determine the value of the information. Bing has a unique approach in rewarding pages that heavily utilize clear and straightforward SEO best practices.
4. Speed and Frequency of Reindexing
The speed at which search engines re-index content can greatly affect how soon changes to a website are reflected in search results. Google’s indexation frequency is typically faster due to its broader crawling capabilities and more frequently updated index, making it more responsive to changes. Bing’s reindexing might be slower, often implying that updates on websites take longer to appear in Bing search results compared to Google.
5. Impact of Technical SEO Components
Technical SEO and its components such as sitemaps, robots.txt, and canonical tags play a significant role in both Google and Bing. Google offers more specialized webmaster tools and guidelines, providing in-depth diagnostics for site owners. While Bing also recognizes these technical structures, it tends to have a different approach and gives additional importance to user engagement and CTR (Click-Through Rate) signals in its ranking and indexation process.
| Feature | Bing | |
|---|---|---|
| Crawler Name | Googlebot | Bingbot |
| JavaScript Handling | Advanced, constant improvement | Improving, less capable |
| Content Quality Factors | Focus on E-A-T | Relevance and social signals |
| Reindexing Speed | Fast | Slower |
| Technical SEO Importance | Detailed tools and support | Emphasizes user engagement |
How is Bing different than Google?
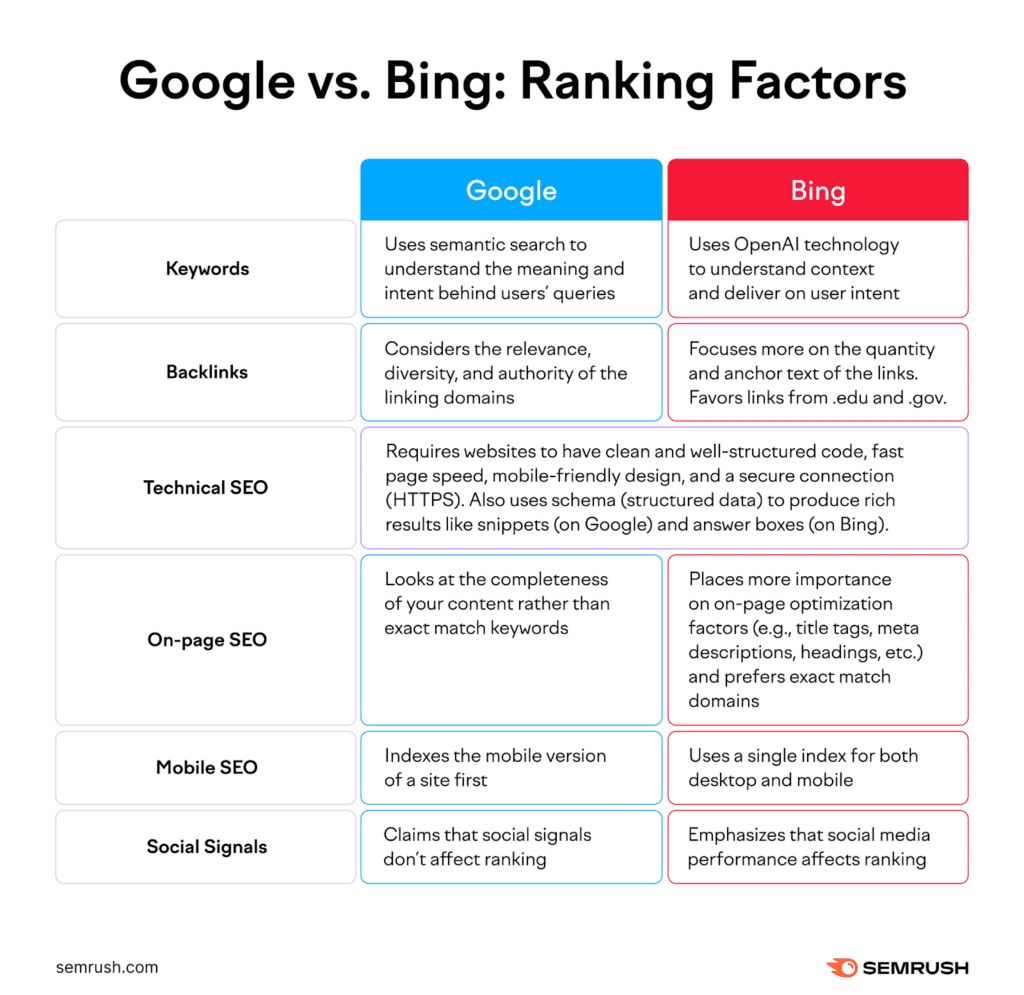
Search Algorithm and Ranking System
Bing and Google use different search algorithms and ranking systems that impact the way search results are delivered to users.
- Indexing Methods: Bing tends to emphasize the latest pages and uses different metrics to evaluate site relevance.
- Ranking Factors: Both engines prioritize quality and authority, but Bing places more emphasis on social signals and local optimization.
- Algorithm Updates: Google’s frequent updates, such as Penguin and Hummingbird, have specific targets, while Bing updates less frequently but focuses on overall enhancements.
User Interface and Features
The user interface and features differ significantly between Bing and Google, affecting usability and user experience.
- Visual Search: Bing offers a visually rich search experience, integrating image previews and multimedia.
- User Experience: Google is known for a minimalist design, whereas Bing provides vibrant, image-laden backgrounds.
- Search Integration: Bing integrates seamlessly with Microsoft products, enhancing productivity for users within the Microsoft ecosystem.
Market Share and Demographics
The market share and user demographics of Bing and Google reveal differences in their popularity and user base.
- Market Penetration: Google holds a dominant share globally, while Bing is particularly strong in North America and the UK.
- Audience Demographics: Bing attracts an older, wealthier user base compared to Google’s more diverse audience.
- Brand Loyalty: Google’s integration with Android and other services contributes to its higher user retention.
Which search engine has the biggest index?

As of the latest available information up to October 2023, Google is widely regarded as having the biggest index among search engines. With over a trillion web pages indexed, Google uses sophisticated algorithms to continuously crawl and expand its database. This extensive indexing allows users to access a broad array of content on virtually any subject imaginable.
How Does Google Achieve the Largest Index?
Google’s ability to maintain the largest index involves several key strategies:
- Web Crawling Technology: Google uses its own web crawlers, popularly known as Googlebot, to explore the web nonstop, discovering new and updated web pages, and ensuring the index remains comprehensive.
- Algorithmic Efficiency: Sophisticated algorithms allow Google to prioritize which pages need indexing and updating, ensuring the most relevant and timely content is available to users.
- Data Centers: With numerous data centers across the globe, Google is able to distribute the storage and processing of its vast index, enhancing both capacity and speed for users worldwide.
Comparison with Other Search Engines
While other search engines also maintain significant web indexes, Google stands out in several ways:
- Breadth of Coverage: Compared to competitors like Bing and Yahoo, Google’s index covers more languages and regions, offering broader global accessibility.
- Frequency of Updates: Google’s infrastructure allows for more frequent updates to its index, providing more current search results than some alternatives.
- Market Share Influence: Given its dominant market share, Google is often prioritized by content creators, encouraging frequent submission and optimization which further supports its expansive index.
Impact of Google’s Large Index on Users
The size of Google’s index directly benefits its users through various aspects:
- Relevance of Results: With more indexed pages, Google can return highly relevant results even for niche or obscure queries.
- Variety of Content Types: Google’s index includes not just web pages but also images, videos, news, and more, providing diverse information formats.
- Search Speed and Efficiency: The depth of Google’s index allows for rapid returns on complex queries, improving the overall user search experience.
What differences did you notice between the search results on Google and Bing?

User Interface and Experience
The user interface and experience notably differ between Google and Bing.
- Google’s Minimalistic Design: Google is recognized for its clean and straightforward design, which emphasizes the search box and results, minimizing distractions.
- Bing’s Visual Appeal: Bing often incorporates visual backgrounds and graphics, making the interface more visually appealing to some users but potentially distracting for others.
- Feature Integration: Google integrates its services directly into its search results, such as calendar entries or flight information, providing a seamless user experience. Bing offers rapid access to Microsoft services like Office or Skype.
Search Result Accuracy and Relevance
The accuracy and relevance of search results are critical for a search engine’s effectiveness.
- Google’s Algorithm: Google’s search algorithm is often perceived as more refined, delivering highly relevant results promptly through advanced indexing and machine learning techniques.
- Bing’s Focus on Multimedia: Bing places a greater emphasis on multimedia, such as images and videos, and often prioritizes these in search results, which can be advantageous for visual searches.
- Local and Voice Searches: Google generally excels in handling local and voice-based searches, thanks in part to its vast data set and natural language processing advancements.
Advertising and Sponsored Content
The presence and treatment of advertising and sponsored content differ between the two platforms.
- Google Ads Prevalence: Google incorporates a significant number of sponsored ads, especially at the top and bottom of search results, often seamlessly interwoven with organic results.
- Bing’s Distinct Ad Placement: Bing’s sponsored results are usually more visibly separated from organic search results, making it easier for users to discern between paid and organic content.
- Ad Quality and Relevance: Both platforms use sophisticated mechanisms to ensure ad relevance, but Google’s larger advertiser ecosystem provides a broader variety of advertisements tailored to user interests.
What happens during Google's indexation process?
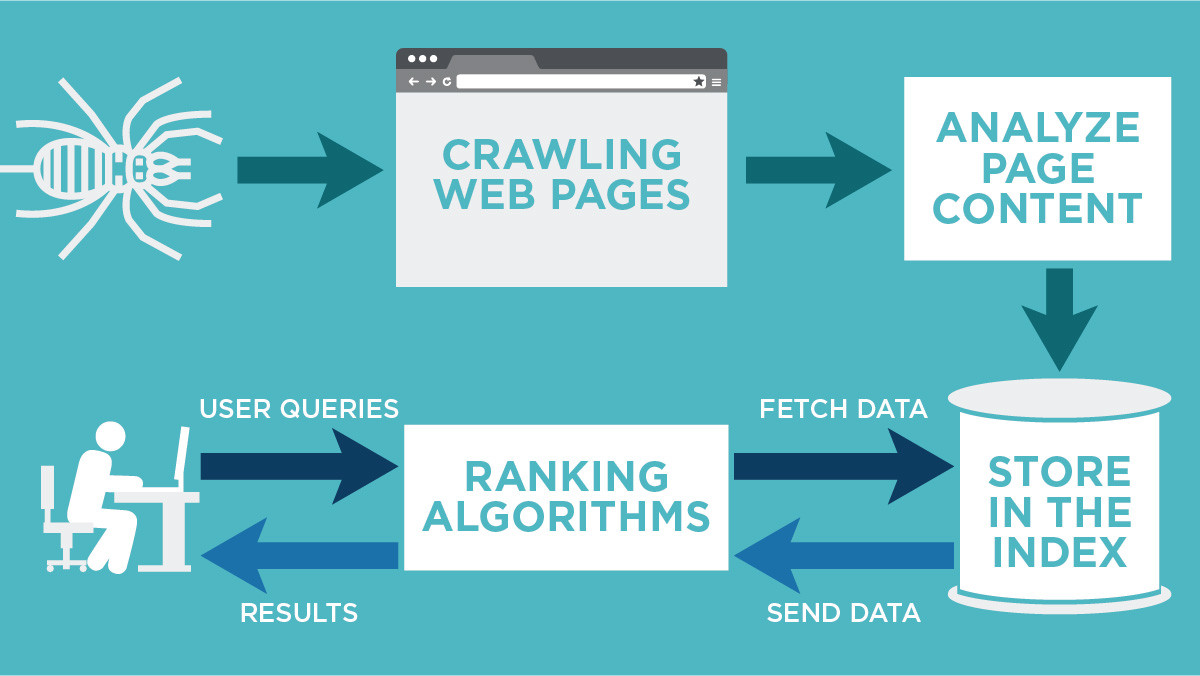
What is Google’s Indexation Process?
Google’s indexation process involves multiple stages through which the search engine systematically analyzes, catalogs, and stores web pages, making them accessible during search queries. The entire process ensures users receive the most relevant and high-quality search results.
- Crawling: Google’s bots explore the web by following links to discover new and updated pages. Crawling starts from previously indexed pages and expands through various hyperlinks.
- Parsing: During this stage, Google’s algorithms analyze the content structure, examining elements like HTML code, keyword placement, link structure, and meta tags to understand the page’s theme and topic.
- Storing: The gathered information is then stored on Google’s servers, effectively organizing data in a structured format within the search index, allowing efficient retrieval during search queries.
How Does Google Decide What to Index?
The decision on what to index is crucial for ensuring the relevance and quality of search results. While Google aims to index as many pages as possible, certain criteria influence this decision.
- Relevancy: Pages must have relevant, valuable content that aligns with user queries. Google favors sites with high keyword relevance and unique information.
- Quality Content: Content quality is assessed through factors like originality, comprehensiveness, and text formatting. Pages with low quality or duplicate content might not be indexed.
- Technical Factors: Proper use of HTML tags, mobile compatibility, and fast loading speeds improve a page’s chances for indexation. Websites should also have proper DNS handling and server availability.
Challenges in the Indexation Process
The indexation process is not without challenges. Various factors can hinder how Google systematically indexes and stores content.
- Duplicate Content: Pages with identical or similar content can confuse Google during crawling, often leading to only one version being indexed or ignored altogether.
- Blocked Pages: Incorrect robots.txt settings or meta tags set to noindex can unintentionally prevent Google from indexing specific web pages, reducing visibility in search results.
- JavaScript Dependency: Sites that heavily rely on JavaScript for content rendering might pose problems; if Googlebot cannot effectively execute the scripts, key content might be missed during crawling.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do Google and Bing handle indexation differently?
Google and Bing use distinct algorithms and crawling methods for indexation, which result in differences in how they process and offer content in search results. Google’s indexation approach is known for its speed and efficiency, optimizing a comprehensive and frequently updated search index. It uses advanced technologies like Mobile-First Indexing, where the mobile version of a website is used for indexing and ranking. Conversely, Bing takes into account certain specific signals differently, such as reliance on URL keywords and social media signals. Bing emphasizes these elements more heavily than Google, potentially leading to different indexing outcomes. This means that while Google might favor fresh, mobile-friendly content, Bing might index content that demonstrates strong social engagement.
What is the role of sitemaps in Google and Bing indexation?
Sitemaps play a crucial role in how both Google and Bing index a website, but their impact can diverge based on each engine’s priorities. For Google, submitting a sitemap can help ensure that new and updated pages are quickly found and indexed. Google’s algorithm is adept at discovering and indexing pages beyond those listed in a sitemap due to its more extensive web crawling capabilities. Bing, however, relies more significantly on the submission of XML sitemaps, often using them as a roadmap to understand the structure of a website. This reliance can help Bing in ensuring that it indexes all pages that webmasters consider important. While both search engines use sitemaps to complement their crawling, the nuances in their reliance can impact indexation behaviors.
In what ways do Google and Bing differ with regard to updates and frequency of indexation?
The frequency and approach to updates in indexation differ notably between Google and Bing. Google is known for its continuous updating process, which often results in pages being indexed and re-indexed with high frequency. It uses technologies such as incremental indexing that allow for rapid reflections of web changes. Bing, on the other hand, updates its index less frequently than Google, relying on a periodic index refresh cycle, which might delay the indexing of some newly updated content. This difference means that for website owners relying on rapid content dissemination, Google typically offers quicker visibility. However, for Bing, understanding the cycles and aligning content updates can ensure optimization in Bing’s periodic update schedule.
How do user engagement metrics affect indexation in Google versus Bing?
User engagement metrics have varying impacts on indexation strategies employed by Google and Bing. Google uses user engagement signals like bounce rate, time on site, and page speed indirectly to assess the quality of content and refine its rankings after initial indexation. However, these factors more influence ranking rather than indexation directly. Bing, however, places a stronger emphasis on user engagement as a part of its initial indexation process. Metrics such as click-through rate (CTR) and user interaction can have a more visible impact on whether and how content is indexed. The effects of these engagement metrics shape how search engines prioritize pages; Google filters this through a quality-focused lens, while Bing uses engagement as a more pronounced direct indexation signal.

