In the intricate world of search engine optimization, the journey from a newly crawled webpage to achieving a high-ranking position is pivotal. Yet, often overlooked in this process is the crucial step of indexing. delves into how indexing serves as the unsung hero that bridges crawling and ranking. This article explores the mechanisms through which search engines interpret and organize content, highlighting why effective indexing strategies are imperative for ensuring that crawled data transforms into ranked authority. Understand the impact of indexing on visibility and learn how to optimize this process.
Understanding the Role of Indexing in Search Engine Optimization
Search engine optimization (SEO) involves multiple steps that are critical for ensuring that a website becomes visible to users performing searches. While crawling and ranking are often highlighted stages, indexing serves as the pivotal intermediary phase. Understanding indexing’s role involves delving into how search engines comprehensively organize and store web data, essentially forming the bridge between being crawled and finally ranked.
The Importance of Indexing in Search Engines
Indexing is a critical component of the SEO process as it involves the search engine’s ability to read, understand, and store information from web pages it has crawled. Without this step, any information a crawler finds is effectively invisible. During indexing, the contents and metadata of a page are organized into a structured database, allowing for efficient retrieval when relevant queries are made. It ensures that the URL is analyzed and subsequently stored in appropriate categories, making it accessible to algorithms responsible for ranking.
How Search Engines Index Web Pages
Search engines utilize complex algorithms to scan and categorize content on the internet. The indexing process involves parsing the HTML code of a webpage, extracting keywords, content length, media elements, and metadata to build a comprehensive profile. This profile helps determine the relevancy and context of a page relative to potential search queries. Additionally, structured data and sitemaps contribute significantly by signaling important information and page hierarchies, enhancing the efficiency of the indexing process.
Common Indexing Challenges and Solutions
Websites often face several challenges in the indexing phase, including duplicate content, poor site architecture, and insufficient internal or external linking. These issues can prevent pages from being indexed properly or cause them to be omitted from results altogether. Solutions involve ensuring that each page has a unique, canonical URL, optimizing website structure for easy navigation, and implementing comprehensive linking strategies. Tools like Google’s Search Console offer insights into indexing status and anomalies, guiding necessary adjustments.
Impact of Indexing on SEO Performance
Proper indexing has a direct influence on a website’s SEO success. If a page is not indexed, it cannot be ranked or appear in search results, nullifying any other SEO efforts. Efficient indexing ensures that pages are visible for their relevant search terms, improving the site’s exposure and traffic potential. Sites with optimized indexing tend to have higher rankings, better user engagement, and improved click-through rates, all contributing to their overall digital authority and presence.
Future Trends in Indexing Technologies
The future of indexing technologies is being shaped by advancements in AI and machine learning, which promise to make the process faster and more precise. Search engines are increasingly leveraging AI to understand context, semantics, and user intent beyond keyword usage. These technologies aim to enhance the accuracy with which search engines categorize and prioritize web content, potentially leading to more personalized and relevant search experiences. Additionally, the growing complexity of multimedia content is prompting the development of more sophisticated indexing methods to effectively process videos, images, and interactive content.
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Crawling | The process where search engine bots discover and collect data from new or updated web pages. |
| Indexing | Organizing and storing the data collected during crawling into a structured format for easy retrieval. |
| Ranking | Evaluating indexed data to determine the order of relevance in search results. |
What is the difference between crawling indexing and ranking?
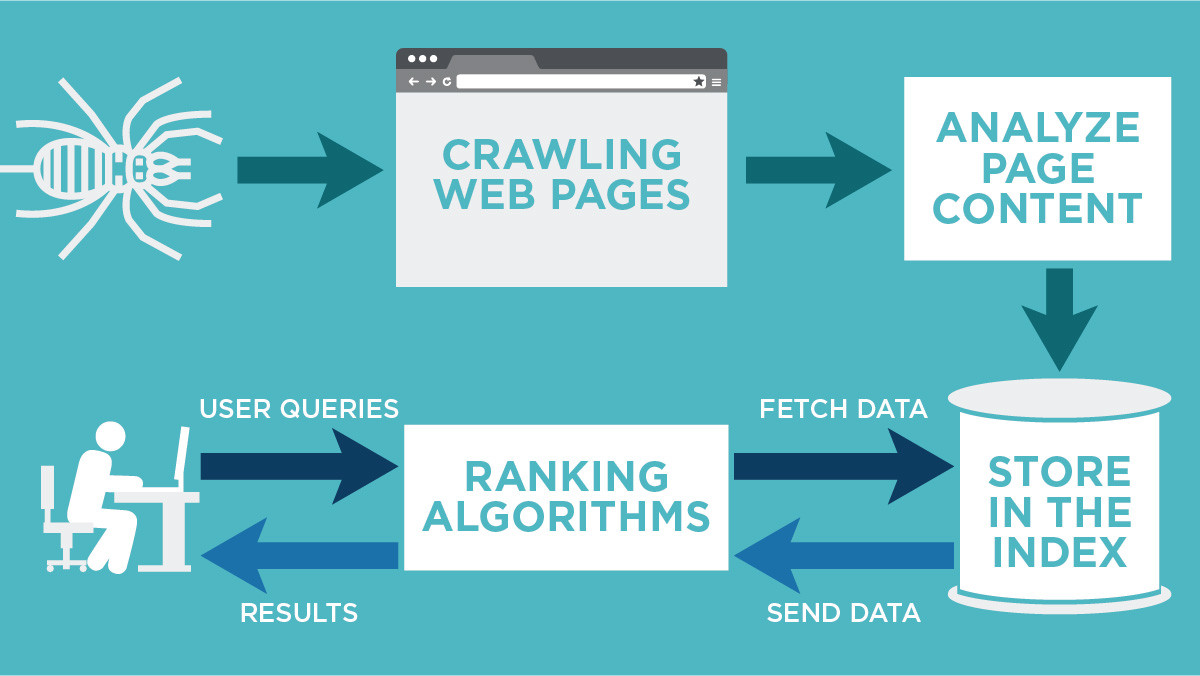
Understanding Crawling in the Search Engine Process
The process of crawling involves search engines discovering new and updated content on the web. Here is how it works and its importance:
- Initiation: A search engine uses bots, known as spiders or crawlers, to identify new or updated pages on the web.
- Discovery: These crawlers follow links within websites and also from one website to another, amassing data about web pages.
- Collection: The crawlers collect URLs and related metadata which are then sent back to the search engine’s servers for indexing.
The Role of Indexing in Search Engines
Indexing is the step that follows crawling, where a search engine processes and stores the information found on webpages. Here’s what happens:
- Storage: The content from crawled pages is organized and stored in a vast database.
- Analysis: The content is analyzed to understand its topics, keywords, and overall relevancy.
- Cataloging: Data is categorized under different topics so it can be quickly retrieved to respond to search queries.
How Ranking Determines Search Engine Results
Ranking is the process where search engines order search results by relevance. It is essential in ensuring users find the most pertinent information quickly:
- Relevancy Scoring: Each indexed page is assigned a score based on how well it matches search queries using algorithms.
- Algorithm Factors: Algorithms consider factors like keyword usage, page quality, user engagement, and domain authority.
- Results Ordering: Pages are then organized in a sequence based on their scores, with higher-ranked results showing up at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs).
Why is my page crawled but not indexed?
Low-Quality Content
Pages may be crawled but not indexed due to low-quality content. Search engines evaluate the relevance and utility of the content before deciding to index it. Here are some factors that might contribute to low-quality content:
- Duplicate Content: If your content is a copy of what already exists online, this could lead to non-indexing.
- Thin Content: Pages with insufficient or overly simplistic content that do not add value to users might not be indexed.
- Poorly Written Content: Content with grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, or incoherent language can be perceived as low-quality.
Crawl Budget Limitations
Your page might be crawled but not indexed because of crawl budget limitations. The crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine will crawl on a website within a given timeframe. Factors affecting this include:
- Large Website Size: Websites with a large number of pages can experience limited crawling opportunities for new content.
- Duplicate Pages: If there are many duplicated or similar pages, these can consume the crawl budget, leaving new pages uncrawled.
- Server Performance: Slow server response times can waste crawl budget as the crawler has less time to index additional pages.
Technical Issues
Technical issues can prevent a page from being indexed even if it gets crawled. Certain technical details to consider are:
- Robots.txt Configuration: Incorrectly setting up your robots.txt file can inadvertently block pages from being indexed.
- Meta Tags: If the page has a ‘noindex’ meta tag, it will be excluded from being added to the index.
- Canonical Tags: Improper use of canonical tags can tell search engines to prioritize other pages, leading to non-indexing of the page in question.
Is crawling the same as indexing?

Crawling and indexing are two fundamental processes in the functioning of search engines, yet they are distinct from each other.
What is Crawling?
Crawling is the process by which search engines discover new and updated pages on the web. This process involves the use of automated bots, often referred to as spiders or crawlers, which systematically browse the internet to collect data about webpages.
- The purpose of crawling is to gather data on various web pages.
- Crawlers analyze pages based on links, going from one page to another by following these links.
- This process helps build a map of the web, which is crucial for further processing in search engines.
What is Indexing?
Indexing is the next step after crawling. It involves storing and organizing the information collected by crawlers from web pages, making them accessible for subsequent search queries conducted by users.
- The purpose of indexing is to organize data to facilitate quick retrieval by the search engine when answering a user query.
- During indexing, important elements such as keywords, metadata, and the overall content of the page are analyzed and recorded.
- Indexed pages are added to a database, which search engines use to deliver relevant results to users.
Key Differences Between Crawling and Indexing
Understanding the distinctions between crawling and indexing helps in optimizing for search engines more effectively.
- Crawling is about discovering web content, while indexing involves storing and organizing that information.
- Crawling is conducted by bots, whereas indexing is more about the processing of collected data into a searchable format.
- The end goal of crawling is to find pages, whereas the goal of indexing is to make pages findable through search queries.
What happens first, crawling or indexing?

Crawling generally occurs before indexing. Crawling is the process where search engine bots discover and scan new or updated content, while indexing is when the scanned content is analyzed and stored in a database, making it eligible to appear in search engine results.
What is Crawling?
Crawling is the initial step in the process where search engines discover content on the internet. This step involves the use of automated scripts or bots, often referred to as web crawlers or spiders. The purpose of crawling is to find new and updated content.
- Crawl Bots: Search engines use specific bots to crawl websites, like Google’s Googlebot, that systematically browse the web.
- Discovery: Crawling helps in discovering new pages and links through following existing links on known pages.
- Identifying Changes: It also includes revisiting pages to check for updates in existing content.
What is Indexing?
Indexing is the subsequent phase after crawling. Once the crawl bots have visited a website and gathered data, that data is then processed and stored in the search engine’s database, which constitutes the index.
- Data Organization: Indexing involves organizing information so it can be quickly retrieved by the search engine.
- Understanding Content: The data is analyzed to understand the nature and quality of the content to assess how relevant it is for potential queries.
- Search Availability: Once indexed, pages become qualifying candidates to appear in search engine results for relevant queries.
The Importance of Crawling Before Indexing
The sequence of crawling before indexing underscores the efficiency and effectiveness of search engines in processing vast amounts of information. Several reasons highlight why crawling is a prerequisite for indexing.
- Data Collection: Crawling is necessary to gather the data needed for further analysis during indexing.
- Content Verification: Ensures that only relevant or updated content is selected, which avoids indexing outdated pages.
- Efficient Resource Use: By confirming availability and relevance through crawling first, search engines optimize resources involved in storing and indexing data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main focus of From Crawled to Ranked: Indexing Is the Missing Link?
The primary focus of From Crawled to Ranked: Indexing Is the Missing Link is to shed light on the critical yet often overlooked step in search engine optimization (SEO) known as indexing. While much emphasis is often placed on the crawling and ranking stages, indexing serves as the crucial intermediary process that determines whether a website’s content will appear in search results. This guide aims to help readers understand why indexing is not just a technical formality but a vital component in ensuring that content reaches its target audience effectively.
Why is indexing considered the ‘missing link’ in the SEO process?
Indexing is referred to as the ‘missing link’ because it bridges the gap between information that has been crawled by search engines and what ultimately gets ranked and displayed in search results. Without proper indexing, even the most valuable content won’t have a chance to appear in user queries. Many SEO strategies fail to acknowledge the importance of indexing, focusing instead on crawling and ranking, thereby missing the crucial step that enables content visibility. This guide argues that understanding and optimizing for the indexing process is essential for successful digital presence.
How does proper indexing impact website visibility?
Proper indexing directly impacts website visibility by determining if and how content is stored within a search engine’s database. If a page fails to be indexed, it becomes effectively invisible to search engine users, regardless of its value or relevance. Successfully indexed pages benefit from better exposure, leading to increased organic traffic and higher engagement. The guide emphasizes that ensuring comprehensive and accurate indexing is fundamental for making sure that content is accessible and served to the right audience.
What strategies can improve the indexing process for a website?
Improving the indexing process can involve several strategies. First, ensuring a clear and logical website architecture enables search engines to more easily crawl and index important pages. Utilizing XML sitemaps and updating them regularly can guide search engines through content changes. Regularly performing technical SEO audits helps identify and rectify any indexing issues, such as duplicate content or poor internal linking. Additionally, keeping content fresh and relevant encourages search engines to revisit and index pages frequently, improving overall site visibility.

