In the digital age, having an online presence is crucial for businesses and content creators alike. However, even the most beautifully designed and content-rich websites can struggle to reach their intended audience if not indexed by search engines. Google, as the dominant search engine, plays a pivotal role in directing the flow of internet traffic. But what happens if your website isn’t included in Google’s index? With billions of pages competing for attention, understanding the implications of not being indexed and how it can impact your visibility, traffic, and ultimately your bottom line, is essential for any online endeavor.
Impact on Your Website When Google Doesn’t Index It
When Google fails to index your website, it essentially means that your site’s pages do not appear in search engine results. This absence can have significant consequences for your site’s visibility and online success. Below are several dimensions explored in detail to understand the implications further.
Why Isn’t My Website Being Indexed?
There are several reasons why Google might not index your website, including technical errors, content issues, or a lack of quality signals. Possible causes include: – Technical Errors: Incorrectly configured robots.txt files, poor website architecture, and meta tags that inadvertently block crawling can all prevent indexing. – Content Duplication: Google may not index your site if it finds the content to be insufficiently original or too similar to other sites. – Low-Quality Content: If your content doesn’t meet Google’s quality guidelines, it might not be indexed. – Lack of Backlinks: Few or no incoming links can lead to a site being overlooked by Google.
What Are the Consequences of Not Being Indexed?
Failing to have your site indexed can lead to: – Reduced Visibility: Not appearing in Google’s search engine results means your website remains largely invisible to potential visitors. – Decreased Traffic: Lower visibility results in fewer visitors, which impacts overall traffic and engagement metrics. – Missed Opportunities: Businesses might miss out on potential sales, leads, and brand recognition due to lack of discoverability. – Damaged Credibility: Consistent absence from search results can harm perceived brand authority and trustworthiness.
How Can I Encourage Google to Index My Website?
To improve the likelihood of your site being indexed, consider the following strategies: – Regular Updates: Frequently updating your content signals to Google that your site is active. – Quality Content: Ensure your site offers unique, valuable, and keyword-optimized content. – Sitemaps: Submit an updated sitemap to Google Search Console to help Google easily locate and understand your pages. – Backlink Building: Increase your site’s authority with high-quality backlinks from reputable sources.
How Long Does It Take for Google to Index a Site?
The indexing timeframe can vary greatly: – Immediate to Few Days: After submission, a site might be indexed relatively quickly if it is straightforward and error-free. – Weeks to Months: More complex sites with many pages, technical errors, or low-quality signals may encounter delays.
How to Monitor If My Site Is Indexed
There are several methods to check your site’s index status: – Google Search Console: This tool provides information on indexed pages and offers opportunities to troubleshoot. – Site Search: Perform a site-specific search (e.g., `site:yourwebsite.com`) to see which pages appear in the results. – Third-Party Tools: Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to monitor specific indexation metrics.
| Factor | Impact on Indexing | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Errors | High | Check robots.txt and meta tags |
| Content Quality | High | Provide unique and valuable content |
| Backlinks | Moderate | Build links from reputable sites |
| Regular Updates | Moderate | Regularly update site content |
| Sitemaps | Moderate | Submit updated sitemap to Google |
Can I force Google to index my site?

While you can’t directly force Google to index your site, there are several strategies to encourage or expedite the process. Google uses algorithms to determine crawling and indexing priorities, but following best practices can positively influence these activities. Here’s how you can improve your chances:
Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a valuable tool for site owners looking to maintain and improve their website’s presence in Google search results. Here’s how you can use it:
- Submit a Sitemap: Ensure you’ve submitted your website’s XML sitemap. This helps Google discover and understand the structure of your website.
- Use the URL Inspection Tool: Use this tool to request indexing of individual URLs. After entering your URL, you can check the last date it was indexed and request Google to index it if needed.
- Monitor Coverage Reports: These reports highlight any crawling or indexing issues that Google encountered. Resolving these issues is crucial for improving your site’s visibility.
Optimizing Website to Improve Crawling
To increase the likelihood of Google crawling and indexing your site more efficiently, focus on optimization:
- Improve Site Speed: Fast-loading sites are more likely to be crawled frequently and thoroughly.
- Ensure Mobile-Friendliness: With Google’s mobile-first indexing, ensuring your site is responsive and performs well on mobile devices is essential.
- Create High-Quality Content: Unique, valuable content encourages regular crawling and indexing by providing a steady stream of new information for Google to index.
Building Quality Backlinks
Backlinks from reputable sites can signal to Google that your site is worth indexing:
- Engage With Guest Blogging: Writing for other reputable sites can provide backlinks that improve your site’s credibility.
- Network With Influencers: Establish connections with key industry players who might link to your site, increasing its authority.
- Leverage Social Media: Promoting your content on social platforms can indirectly lead to more backlinks as your content gains visibility.
Should I index my website on Google?

Indexing your website on Google is a crucial step if you want to make your site visible to a broad audience. Once indexed, your site can appear in search results, which is fundamental for gaining organic traffic and reaching potential visitors. Without indexing, your site will remain invisible to most internet users who rely on search engines for discovering content.
Why is Indexing Important for Your Website?
Indexing is essential for several reasons that enhance the presence and utility of your website:
- Visibility: Once indexed, your website appears in search results, providing access to millions of users searching for relevant content.
- Credibility: Websites found via Google often gain more trust from users due to the search engine’s reputation for delivering relevant and accurate information.
- Traffic: Indexed websites generally receive more organic traffic, which is essential for growth and engagement.
How to Check If Your Site is Indexed by Google
Knowing if your site is indexed by Google helps ensure that your SEO efforts are effectively reaching your audience:
- Search for Your URL: Use Google and type site:yourdomain.com. This will show you all pages Google has indexed.
- Google Search Console: Sign up for and use Google Search Console to get comprehensive data on how your site is indexed.
- Manual Inspection: Navigate through your site’s search presence by checking manually in Google search results.
Steps to Effectively Index Your Website
Proper indexing can be achieved by following key strategies that improve website recognition:
- Submit a Sitemap: Create and submit a sitemap to Google Search Console to inform Google about the pages on your site.
- Ensure Quality Content: Regularly update your site with unique, relevant, and quality content that is more likely to be indexed quickly.
- Enhance Linking: Utilize internal and external linking strategies to ensure all pages are accessible and encourage Google’s crawlers to explore your site.
What does it mean when a website is not indexed?
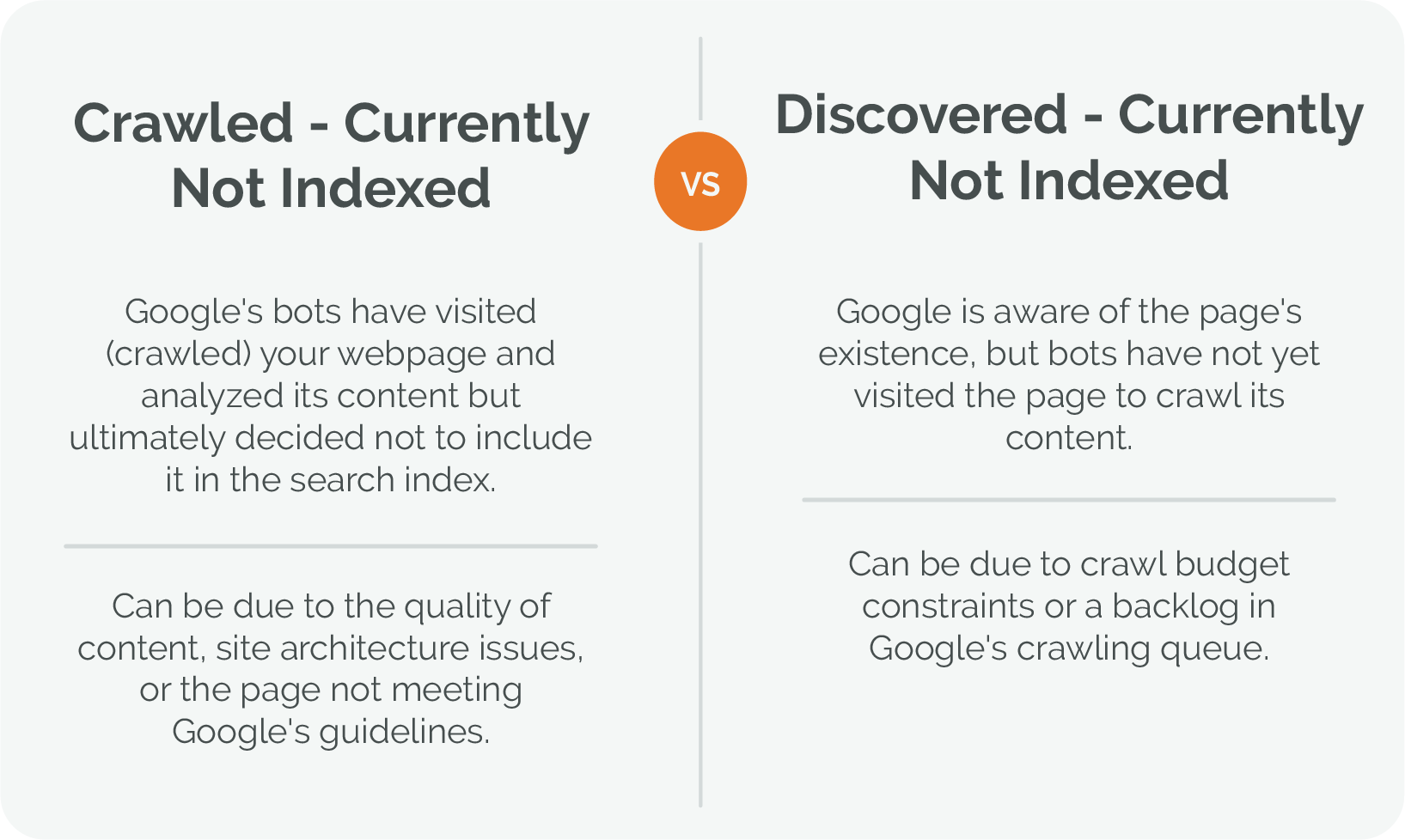
When a website is not indexed, it means that the pages of that site are not stored in the database of a search engine. As a result, the search engine does not show any results from that website when users perform related searches. Indexing is a crucial step in ensuring that a website is visible and discoverable via search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. Without indexing, even the most well-designed website remains invisible to anyone conducting an online search for its content.
Reasons a Website May Not Be Indexed
Several factors can prevent a website from being indexed by search engines:
- Crawling Issues: If search engines cannot access a website due to server errors, slow loading times, or erroneous robots.txt files, they cannot index it.
- Content Quality: Websites with low-quality content or duplicate content may not be indexed. Search engines prioritize unique and valuable content.
- Manual Actions: Sometimes, search engines manually prevent a site from being indexed due to policy violations, such as spammy content or manipulative practices.
Implications of Not Being Indexed
Not being indexed has several significant implications for websites:
- Reduced Visibility: The primary implication is a significant reduction in visibility. Without indexing, potential visitors may not find the website through search engines.
- Traffic Loss: A reduction in visibility directly influences website traffic. Lower search engine traffic can lead to fewer leads, conversions, and sales.
- Brand Awareness: Unindexed websites lose out on opportunities for brand exposure and awareness, limiting their potential audience.
Steps to Ensure a Website is Indexed
To increase the chances of a website being indexed, consider the following steps:
- Submit a Sitemap: Providing search engines with a comprehensive sitemap optimizes crawling efficiency and ensures all pages are recognized.
- Optimize Content: Ensure that content is high-quality, unique, and relevant. This increases the likelihood of it being favorably indexed by search engines.
- Regular Audits: Regularly check and resolve any technical issues that might impact indexing, such as broken links or server errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean if Google doesn’t index your website?
If Google doesn’t index your website, it means that the search engine hasn’t included your web pages in its database or index, which is crucial for those pages to appear in search results. Without being indexed, your site cannot be discovered through organic search, which can significantly impact your traffic and visibility. This typically occurs due to technical issues such as blocking methods in your site’s robots.txt, incorrect meta tags, or because the content is seen as lacking value or relevance. Ensuring that Google indexes your site is essential for search presence, so identifying and addressing any barriers is critical.
Why is indexing important for SEO?
Indexing is crucial for SEO because it directly affects your website’s visibility and discoverability on search engines. When your site is indexed, it becomes part of the search engine’s database, allowing it to be displayed in SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) when users query related topics. This can lead to increased traffic, higher rankings, and better brand exposure. Without indexing, even the most compelling website with valuable content won’t reach its potential audience, highlighting the importance of proper indexing for any effective SEO strategy.
How can you check if your pages are indexed by Google?
You can check if your pages are indexed by Google using several methods. One of the simplest ways is to conduct a site search by typing “site:yourdomain.com” into the Google search bar, which will display indexed pages under that domain. Another method is using Google Search Console, which provides a comprehensive overview of your site’s indexing status. It helps to identify which pages are indexed and highlights any issues preventing indexing. Monitoring these aspects can help ensure your site’s health and improve its performance in search results.
What steps should you take if your website is not indexed?
If your website is not indexed, there are several steps you can take to address the issue. First, use Google Search Console to identify any errors or warnings. Ensure your site is not inadvertently blocked from indexing by reviewing your robots.txt file and meta tags for the noindex directive. Address any technical issues like slow page load times or mobile incompatibility. Additionally, create and submit an XML sitemap to Google, and consider updating your content to be more engaging or relevant. Establish backlinks from reputable sites, as this can signal to Google that your site is valued and worthy of indexing. Following these actions can help facilitate the indexing process and improve your search presence.

